Answer:
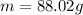
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello there!
In this case, for this ideal gas law problem, it turns out necessary for us to remember that one mole of any gas is contained in 22.4 L at STP and therefore, we can use the following ratio to calculate the moles in 44.8 L of CO2:
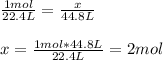
Finally, since the molar mass of CO2 is 44.01 g/mol, we calculate the mass as follows:
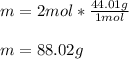
Regards!