Answer: The electron number density (the number of electrons per unit volume) in the wire is
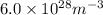 .
.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given: Current = 5.0 A
Area =
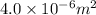
Density = 2.7
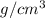 , Molar mass = 27 g
, Molar mass = 27 g
The electron density is calculated as follows.
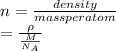
where,
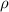 = density
= density
M = molar mass
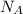 = Avogadro's number
= Avogadro's number
Substitute the values into above formula as follows.
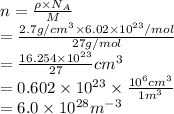
Thus, we can conclude that the electron number density (the number of electrons per unit volume) in the wire is
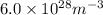 .
.