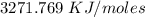Answer:
The right solution is:
(a) 2459.74 J/degree C
(b) 3271.769 KJ/moles
Step-by-step explanation:
According to the question,
(a)
The heat capacity of the calorimeter will be:
=
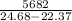
=
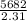
=
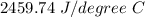
(b)
The change in temperature will be:
=
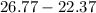
=
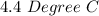
The amount of heat released will be:
=
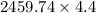
=
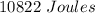
or,
=
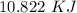
Moles of benzene combusted will be:
=
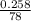
=
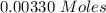
hence,
The heat combustion for 1 mol of benzene will be:
=
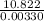
=