The question is incomplete, the complete question is:
The solubility of slaked lime,
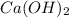 , in water is 0.185 g/100 ml. You will need to calculate the volume of
, in water is 0.185 g/100 ml. You will need to calculate the volume of
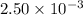 M HCl needed to neutralize 14.5 mL of a saturated
M HCl needed to neutralize 14.5 mL of a saturated
Answer: The volume of HCl required is 290mL, the mass of
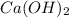 is 0.0268g, the moles of
is 0.0268g, the moles of
Step-by-step explanation:
Given values:
Solubility of
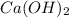 = 0.185 g/100 mL
= 0.185 g/100 mL
Volume of
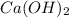 = 14.5 mL
= 14.5 mL
Using unitary method:
In 100 mL, the mass of
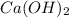 present is 0.185 g
present is 0.185 g
So, in 14.5mL. the mass of
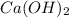 present will be =
present will be =
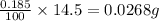
The number of moles is defined as the ratio of the mass of a substance to its molar mass.
The equation used is:
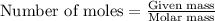 ......(1)
......(1)
Given mass of
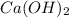 = 0.0268 g
= 0.0268 g
Molar mass of
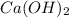 = 74 g/mol
= 74 g/mol
Plugging values in equation 1:
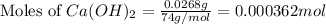
Moles of
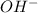 present =
present =
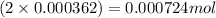
The chemical equation for the neutralization of calcium hydroxide and HCl follows:
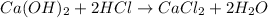
By the stoichiometry of the reaction:
Moles of
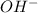 = Moles of
= Moles of
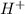 = 0.000724 mol
= 0.000724 mol
The formula used to calculate molarity:
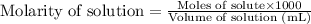 .....(2)
.....(2)
Moles of HCl = 0.000724 mol
Molarity of HCl =
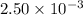
Putting values in equation 2, we get:
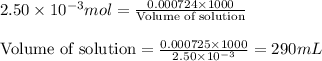
Hence, the volume of HCl required is 290mL, the mass of
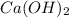 is 0.0268g, the moles of
is 0.0268g, the moles of