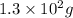The question is incomplete, the complete question is:
A certain substance X has a normal freezing point of
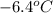 and a molal freezing point depression constant
and a molal freezing point depression constant
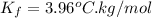 . A solution is prepared by dissolving some glycine in 950. g of X. This solution freezes at
. A solution is prepared by dissolving some glycine in 950. g of X. This solution freezes at
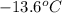 . Calculate the mass of urea that was dissolved. Round your answer to 2 significant digits.
. Calculate the mass of urea that was dissolved. Round your answer to 2 significant digits.
Answer: The mass of glycine that can be dissolved is
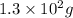
Step-by-step explanation:
Depression in the freezing point is defined as the difference between the freezing point of the pure solvent and the freezing point of the solution.
The expression for the calculation of depression in freezing point is:
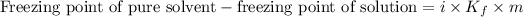
OR
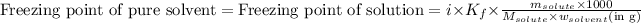 ......(1)
......(1)
where,
Freezing point of pure solvent =
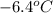
Freezing point of solution =
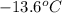
i = Vant Hoff factor = 1 (for non-electrolytes)
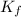 = freezing point depression constant =
= freezing point depression constant =
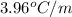
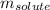 = Given mass of solute (glycine) = ?
= Given mass of solute (glycine) = ?
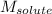 = Molar mass of solute (glycine) = 75.07 g/mol
= Molar mass of solute (glycine) = 75.07 g/mol
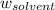 = Mass of solvent = 950. g
= Mass of solvent = 950. g
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
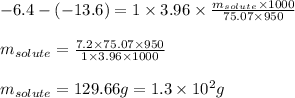
Hence, the mass of glycine that can be dissolved is