Answer:
1. The tightness of the wire has no effect on the strength of the electromagnet
2. The strength increases with the number of coils
3. The strength of the electromagnet increases with the number of dry cells used
4. The strength of the electromagnet increases with the wideness of the nail but not the length of the nail
Step-by-step explanation:
The strength of an electromagnet is given by the following relation;
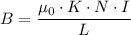
Where;
B = The magnetic field strength at the center
μ₀ = The magnetic permeability of free space = 4·π × 10⁻⁷ N·A⁻²
N = The number of loops formed by the conductor around the core
I = The current flowing through wire coiled around the nail
K = The magnetic permeability of the nail
L = The length of the coil
Therefore, we have;
1. From the above equation, the tightness of the wire coil around the nail (or the radius, 'R', of the wire) does not does not affect the magnetic field strength
2. The number of coils, 'N', is directly related to the magnetic field strength, 'B', and therefore, increasing the number of turns or coils around the nail, increases the magnetic field strength
3. The current in the circuit is directly related to the magnetic field strength and the number of dry cell used increases the current in the circuit and therefore, can increase the magnetic field strength
4. The size of the nail used in a solenoid and the magnetic field strength are directly related. The wider the nail, the stronger the magnetic field