Answer: The number of moles of gas which are present in the sample are 1.49 mol.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given: Volume = 55.3 L
Temperature =
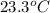 = (23.3 + 273) K = 296.3 K
= (23.3 + 273) K = 296.3 K
Pressure = 0.658 atm
Formula used is as follows.
PV = nRT
where,
P = pressure
V = volume
n = no. of moles
R = gas constant = 0.0821 L atm/mol K
T = temperature
Substitute the values into above formula as follows.
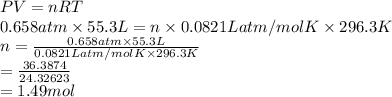
Thus, we can conclude that the number of moles of gas which are present in the sample are 1.49 mol.