Answer:
(b) cosine
Step-by-step explanation:
In a 2-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system, a vector has a x-component and/or a y-component. To get these components, the magnitude of the vector is resolved with respect to the x-axis and the y-axis by multiplying it (the magnitude) by some trigonometric function with respect to the angle between the vector and the x or y axis.
For example, given a vector A of magnitude A which makes an angle α with the x-axis and an angle β with the y-axis, the x and y components of the vector A can be found as follows;
i. x-component is given by
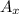
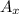 = A cos α (with respect to the angle between A and the x-axis) or
= A cos α (with respect to the angle between A and the x-axis) or
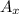 = A sin β (with respect to the angle between A and the y-axis)
= A sin β (with respect to the angle between A and the y-axis)
ii. y-component is given by
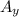
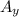 = A sin α (with respect to the angle between A and the x-axis) or
= A sin α (with respect to the angle between A and the x-axis) or
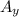 = A cos β (with respect to the angle between A and the y-axis)
= A cos β (with respect to the angle between A and the y-axis)
Therefore, the y-component of a vector in a 2-dimensional Cartesian coordinate is given by the product of the magnitude of the vector and the cosine of the angle between the vector and the y-axis.