Answer:
The answer is below
Step-by-step explanation:
a) The work done is equal to the loss in kinetic energy (KE)
Change in kinetic energy (ΔKE) = Final kinetic energy - initial kinetic energy
Final KE =
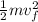
But the final velocity is 0 (at rest). Hence:
Final KE =
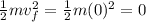
ΔKE = 0 - K = -K
W = ΔKE = -K
Also, the work done (W) = charge (q) * distance (d) * electric field intensity (E)
W = qEd
but q = -e, hence:
W = -e * E * d
Using:
W = ΔKE
-e * E * d = -K
E= K / (e * d)
b) The electric field is in the direction of the electrons motion