a. Calculate elasticity using the derivative of the demand equation.
b. If elasticity > 1 at $3, it's elastic; otherwise, inelastic.
a. To calculate the elasticity of demand (E), we start by finding the derivative of the demand equation q =
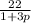 with respect to p. The derivative is
with respect to p. The derivative is
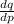 = -
= -
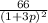 . Now, substitute
. Now, substitute
p=3 into this derivative to get the slope at p=3, giving us the percentage change in quantity demanded concerning a 1% change in price. The result will indicate the elasticity of demand.
b. The interpretation of elasticity involves comparing the calculated value with 1. If the elasticity is greater than 1, it implies an elastic demand, signifying that a 1% increase in price will result in more than a 1% decrease in quantity demanded.
On the other hand, if the elasticity is less than 1, it suggests an inelastic demand, where a 1% change in price leads to a less than 1% change in quantity demanded.
For instance, if the price is $3 and the calculated elasticity is greater than 1, the demand is elastic; otherwise, it is inelastic. Understanding elasticity is crucial for businesses in pricing and revenue management strategies.