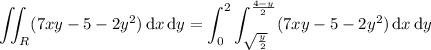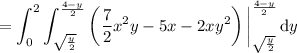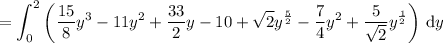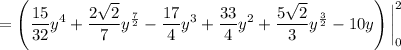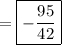Attached you'll find the region of interest, which is captured by the set of points
R = √(y/2) ≤ x ≤ (4 - y)/2 and 0 ≤ y ≤ 2
Written in this way, it's convenient to integrate with the order dx dy (that is, with respect to x first). In particular, we have