Answer:
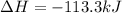
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello there!
In this case, since the reaction for the formation of CO2 is:
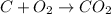
Whereas the determination of the limiting reactant must be firstly performed as shown below:
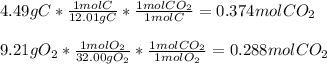
Thus, we infer O2 is the limiting reactant because it yields less moles of CO2 in comparison to C; and therefore, the enthalpy change is:
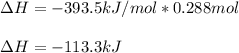
Best regards!