Answer:
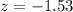 --- test statistic
--- test statistic
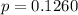 --- p value
--- p value
Conclusion: Fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Explanation:
Given
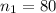


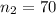
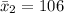

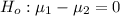 --- Null hypothesis
--- Null hypothesis
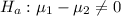 ---- Alternate hypothesis
---- Alternate hypothesis
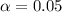
Solving (a): The test statistic
This is calculated as:
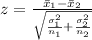
So, we have:
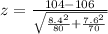
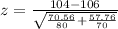
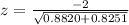
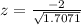
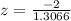
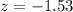
Solving (b): The p value
This is calculated as:
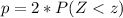
So, we have:
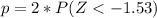
Look up the z probability in the z score table. So, the expression becomes
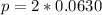
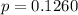
Solving (c): With
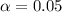 , what is the conclusion based on the p value
, what is the conclusion based on the p value
We have:
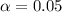
In (b), we have:
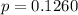
By comparison:
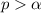
i.e.
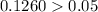
So, we fail to reject the null hypothesis.