Step-by-step explanation:
Given: a = -3v^2
By definition, the acceleration is the time derivative of velocity v:
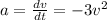
Re-arranging the expression above, we get
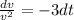
Integrating this expression, we get
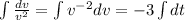
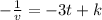
Since v = 10 when t = 0, that gives us k = -1/10. The expression for v can then be written as
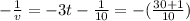
or
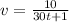
We also know that
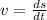
or
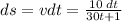
We can integrate this to get s:
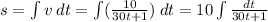
Let u = 30t +1
du = 30dt
so
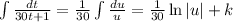
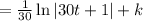
So we can now write s as
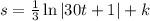
We know that when t = 0, s = 8 m, therefore k = 8 m.
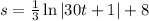
Next, we need to find the position and velocity at t = 3 s. At t = 3 s,
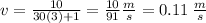
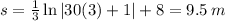
Note: velocity approaches zero as t -->