Answer:
pH = 10.9
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello there!
In this case, according to the given information, it turns out possible for us to say that the undergoing reaction between this buffer and OH⁻ promotes the formation of more CO₃²⁻ because it acts as the base, we can do the following:
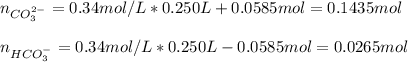
The resulting concentrations are:
![[CO_3^(2-)]=(0.1435mol)/(0.25L)=0.574M \\](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/7hs598wua3aeyf3tlz2aspk3dreqtyyhk5.png)
![[HCO_3^(-)]=(0.0265mol)/(0.25L)=0.106M](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/ysi6nmqo41bkyku169mg2qxqt32lvxisun.png)
Thus, since the pKa of this buffer system is 10.2, the change in the pH would be:
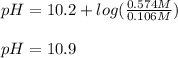
Which makes sense since basic OH⁻ ions were added.
Regards!