Answer:
Equilibrium will be shifted towards NO2 as it has the most of the moles in the reaction.
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello there!
In this case, according to the equilibrium reaction between NO2 and N2O4, we are able to write:
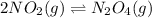
We can recall the LeCha-telier's principle to realize that the increase of volume promotes the formation of the most of the moles, this is for NO2 because it has a coefficient of 2 and N2O4 a coefficient of 1; in such a way, we infer that the addition of argon, to increase the pressure, will shift the equilibrium towards NO2.
Regards!