Answer: The limiting reactant is hydrogen gas and the mass of excess reactant
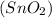 left over is 197.43 g
left over is 197.43 g
Step-by-step explanation:
Limiting reagent is defined as the reagent which is completely consumed in the reaction and limits the formation of the product.
Excess reagent is defined as the reagent which is left behind after the completion of the reaction.
The number of moles is defined as the ratio of the mass of a substance to its molar mass.
The equation used is:
......(1)
We are given:
Given mass of
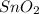 = 351.3 g
= 351.3 g
Molar mass of
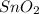 = 150.71 g/mol
= 150.71 g/mol
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
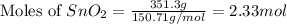
At STP conditions:
22.4 L of volume is occupied by 1 mole of a gas
Applying unitary method:
45.8 L of volume will be occupied by =
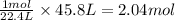 of hydrogen gas
of hydrogen gas
For the given chemical reaction:
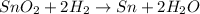
By stoichiometry of the reaction:
If 2 moles of hydrogen gas reacts with 1 mole of
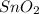
So, 2.04 moles of hydrogen gas will react with =
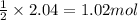 of
of
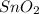
As the given amount of
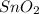 is more than the required amount. Thus, it is present in excess and is considered as an excess reagent.
is more than the required amount. Thus, it is present in excess and is considered as an excess reagent.
Thus, hydrogen gas is considered a limiting reagent because it limits the formation of the product.
Moles of excess reactant (
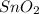 ) left = [2.33 - 1.02] = 1.31 moles
) left = [2.33 - 1.02] = 1.31 moles
We know, molar mass of
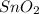 = 150.71 g/mol
= 150.71 g/mol
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
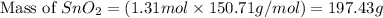
Hence, the limiting reactant is hydrogen gas and the mass of excess reactant
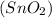 left over is 197.43 g
left over is 197.43 g