Answer:
Explanation:
Given that:
![P = \left[\begin{array}{ccc}0.22&0.20&0.65\\0.62&0.60&0.15\\0.16&0.20&0.20\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/pnd4zyszh9qofpeturw53rvcmwc7298ono.png)
For a steady-state of a given matrix
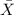
![\bar X = \left[\begin{array}{c}a\\b\\c\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/dxfeqz26ie28p4s3z9f278kbyi41lkoixb.png)
As a result P
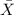 =
=
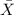 and a+b+c must be equal to 1
and a+b+c must be equal to 1
So, if P
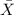 =
=
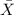
Then;
![P = \left[\begin{array}{ccc}0.22&0.20&0.65\\0.62&0.60&0.15\\0.16&0.20&0.20\end{array}\right]\left[\begin{array}{c}a\\b\\c\end{array}\right] =\left[\begin{array}{c}a\\b\\c\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/r4s2rheq94dfnyr8cq21ptksq78920sczl.png)
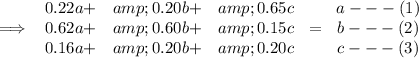
Equating both equation (1) and (3)
(0.22a+ 0.2b + 0.65c) - (0.16a + 0.2b + 0.2c) = a - c
0.06a + 0.45c = a - c
collect like terms
0.06a - a = -c - 0.45c
-0.94 a = -1.45 c
0.94 a = 1.45 c
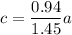
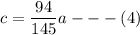
Using equation (2)
0.62a + 0.60b + 0.15c = b
where;
c = 94/145 a
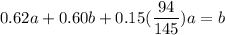
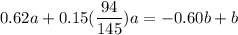
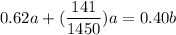
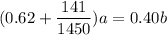
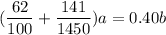
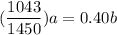
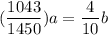
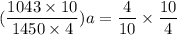
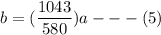
From a + b + c = 1
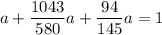
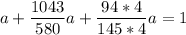
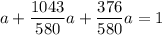
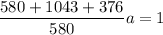
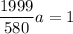
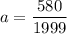
∴
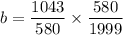
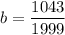
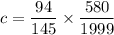
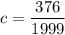
∴
The steady matrix of
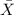 is:
is:
![\bar X = \left[\begin{array}{c}(580)/(1999) \\ \\ (1043)/(1999)\\ \\ (376)/(1999)\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/w8yrludxactu717hyhjcybt5psslb2zke2.png)