Answer: The mass of carbon dioxide required is 308 g
Step-by-step explanation:
The number of moles is defined as the ratio of the mass of a substance to its molar mass.
The equation used is:
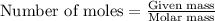 ......(1)
......(1)
Given mass of octane = 100.0 g
Molar mass of octane = 114.23 g/mol
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
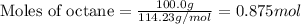
For the given chemical reaction:
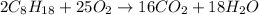
By the stoichiometry of the reaction:
2 moles of octane produces 16 moles of carbon dioxide
So, 0.875 moles of octane will produce =
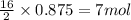 of carbon dioxide
of carbon dioxide
Molar mass of carbon dioxide = 44 g/mol
Plugging values in equation 1:
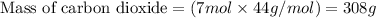
Hence, the mass of carbon dioxide required is 308 g