Answer:
The p-value of the test is 0.0043 < 0.01, which means that it can be concluded that the average differs from the population average.
Explanation:
The average amount of time a person exercises daily is 22.7 minutes in a population. Test if the average differs from the population average.
At the null hypothesis, we test if it does not differ, that is, the mean is of 22.7 minutes. So
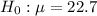
At the alternate hypothesis, we test if it does differ, that is, if the mean is different of 22.7 minutes. So
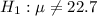
The test statistic is:
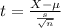
In which X is the sample mean,
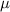 is the value tested at the null hypothesis, s is the standard deviation and n is the size of the sample.
is the value tested at the null hypothesis, s is the standard deviation and n is the size of the sample.
22.7 is tested at the null hypothesis:
This means that
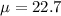
A random sample of 20 people showed an average of 29.8 minutes in time with a standard deviation of 9.8 minutes.
This means that
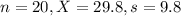
Value of the test statistic:
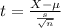
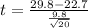
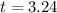
P-value of the test:
Using the t-distribution, testing if the mean is different, so a two-tailed test with t = 3.24 and 20 - 1 = 19 degrees of freedom.
Using a t-distribution calculator, the p-value of the test is of 0.0043.
The p-value of the test is 0.0043 < 0.01, which means that it can be concluded that the average differs from the population average.