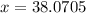Answer:
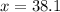
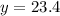
Explanation:
The given triangle is a right triangle. This is indicated by the box around one of the angles, signifying that the angle measure is (9) degrees. By its definition, a right triangle is a triangle with a (90) degree angle, thus the given triangle is a right triangle. In this situation, one can use right-angle trigonometry to find the value of the unknown side. In essence, right triangle trigonometry provides one with a series of ratios to describe the relationship between the sides and angles of the right trinagle. These ratios are the following,
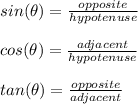
Keep in mind that the way a side is named is relative to the angle it is being described from. Thus, the (opposite) and (adjacent) sides acquire different names based on the angle relative to them. However, the (hypotenuse) is the hypotenuse no matter the angle, as the hypotenuse is the side opposite the right angle.
Solve for (y) first. One is given the angle measure and the measure of the side opposite the angle measure. One is asked to find the measure of the side adjacent to the angle. Use the ratio of tangent (tan) to achieve this.
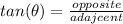
Substitute,
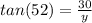
Inverse operations,
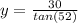
Simplify,
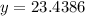
Now solve for the hypotenuse (x). One could use the Pythagorean theorem to do this, but since this is trigonometry, one might as well use the trigonometric ratios. One is given an angle, as well as the side opposite the angle, one is asked to find the hypotenuse. To do this, one can use the trigonometric ratio of sine (sin).
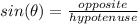
Substitute,
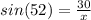
Inverse operations,
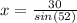
Simplify,