Answer:
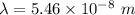
Step-by-step explanation:
The hottest ordinary star in our galaxy has a surface temperature of 53,000 K.
We need to find the peak wavelength of its thermal radiation.
Using Wein's law,
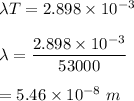
So, the peak wavelength of its thermal radiation is equal to
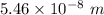 .
.