Solution :
The equation is :
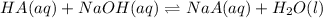
The number of the moles of HA os 0.00285, and the volume is 25 mL.
15 mL of the 0.0950 M NaOH is added.
The total volume of a solution is V = 25 mL + 15 mL = 40 mL
The pH of the solution is 6.50
Calculating the
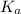 of HA
of HA
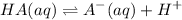
![K_a=([A^-].[H^+])/([HA])](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/v4os81jtgp9hobkk9r4ocz41fg7co9xbbj.png)
Let s calculate the concentration of HA and NaOH
![$[HA] = (^nH_A)/(V)$](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/rgu2gsz7vybwt7m770hoxsrxw0zg66frl5.png)
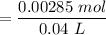
= 0.07125 M
![$[NaOH]= (0.015L * 0.0950 M)/(V)$](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/24ij55u3s75k5bapodan47qsbw66htmrcz.png)
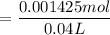
= 0.0356 M

Initial conc. (M) 0.07125 M 0.0356 M 0 M
Change in conc. (M) -0.0356 M -0.0356 M + 0.0356 M
Equilibrium conc. (M) 0.03565 M 0 M 0.0356 M
Therefore, the concentration of HA and the NaA at the equilibrium are [HA] = 0.03565 M and [NaA]= 0.0356 M
0.0356 M of NaA dissociates completely into 0.0356 M
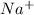 and 0.0356 M
and 0.0356 M
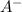
Now for
![[H^+]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/high-school/869xv4va2pom353pcqwbgfhb9dbdu5d2fd.png)
![$[H^+] = 10^(-pH)$](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/ghb6wmj1asrd89xcvkr4f08wiby88p2i6c.png)
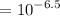
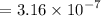
Calculating the value of
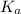 ,
,
![K_a=([A^-].[H^+])/([HA])](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/v4os81jtgp9hobkk9r4ocz41fg7co9xbbj.png)
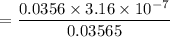
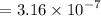
Therefore the the value of
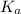 for the unknown acid is
for the unknown acid is
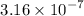 .
.