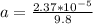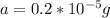Answer:
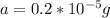
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that:
Mass
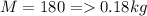
Charge
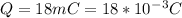
Velocity
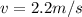
Length of Wire
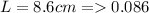
Current
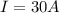
Generally the equation for Magnetic Field of Wire B is mathematically given by
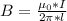
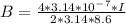
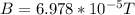
Generally the equation for Force on the plane F is mathematically given by
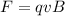
Therefore
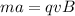
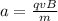
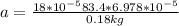
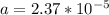
Therefore in Terms of g's