Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
From the given information:
The initial PE
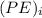 = m×g×h
= m×g×h
= 5 kg × 9.81 m/s² × 10 m
= 490.5 J
The change in Potential energy P.E of the box is:
ΔP.E =
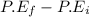
ΔP.E = 0 -
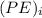
ΔP.E =
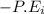
If we take a look at conservation of total energy for determining the change in the internal energy of the box;
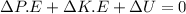
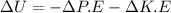
this can be re-written as:
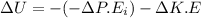
Here, K.E = 0
Also, 70% goes into raising the internal energy for the box;
Thus,
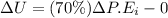
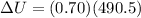
ΔU = 343.35 J
Thus, the magnitude of the increase is = 343.35 J