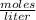Answer:
The molarity of the solution is 1.1
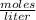
Step-by-step explanation:
Molarity is a measure of the concentration of that substance that is defined as the number of moles of solute divided by the volume of the solution.
The molarity of a solution is calculated by dividing the moles of the solute by the volume of the solution:
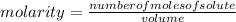
Molarity is expressed in units
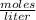
In this case
- number of moles of solute= 0.564 moles
- volume= 0.510 L
Replacing:
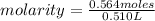
Solving:
molarity= 1.1
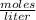
The molarity of the solution is 1.1