The length of BD ≈ 3.6 cm.
The diagram shows a triangle ABC with sides AB = 8.1 cm, AC = 5.9 cm, and CD = 2 cm. We are asked to find the length of side BD and side AD, given that angles DAC and BAD are equal.
Solution:
1. Identify the relevant triangles: We can see two smaller triangles within the larger triangle ABC: triangle ADC and triangle ABD.
2. Apply the Law of Cosines to triangle ADC:
We know AC = 5.9 cm and CD = 2 cm, and we need to find AD. Angle DAC is given as equal to angle BAD, so we can use the Law of Cosines to find AD:
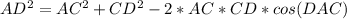
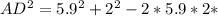 cos(90°) // Since angles DAC and BAD are equal, and triangle ADC is a right triangle, cos(DAC) = 0
cos(90°) // Since angles DAC and BAD are equal, and triangle ADC is a right triangle, cos(DAC) = 0
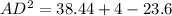
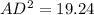
- AD ≈ 4.4 cm (rounded to one decimal place)
3. Apply the Law of Cosines to triangle ABD:
Now that we know AD = 4.4 cm, we can find BD using the Law of Cosines again:
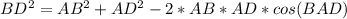
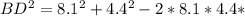 cos(90°)
cos(90°)
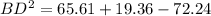
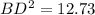
- BD ≈ 3.6 cm (rounded to one decimal place)
Therefore, the length of side BD is approximately 3.6 cm and the length of side AD is approximately 4.4 cm.