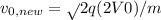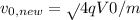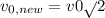Answer:
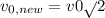
Step-by-step explanation:
Initial work done on the proton is given by,
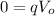
we know that,

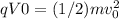
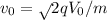 { eq.1 }
{ eq.1 }
If it were accelerated instead through a potential difference of 2V0, then it would gain a speed will be given as :
using the above formula, we have