Answer:
A 11.1%
Explanation:
The students are chosen from a sample without replacement, which means that the hypergeometric distribution is used to solve this question.
Hypergeometric distribution:
The probability of x sucesses is given by the following formula:
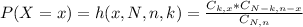
In which:
x is the number of sucesses.
N is the size of the population.
n is the size of the sample.
k is the total number of desired outcomes.
Combinations formula:
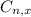 is the number of different combinations of x objects from a set of n elements, given by the following formula.
is the number of different combinations of x objects from a set of n elements, given by the following formula.
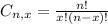
In this question, we have that:
13 + 7 = 20 teachers, which means that N = 20.
7 history teachers means that k = 7.
Two teachers for each student, which means that n = 2.
What is the approximate probability that a random student on the trip will be assigned to a group led by two history teachers?
This is P(X = 2). So
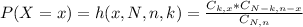
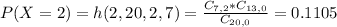
So close to 11.1%, and the correct answer is given by option A.