Answer:
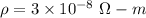
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that,
Voltage, V = 120 V
The length of the wire, l = 20 m
The current density of the wire,
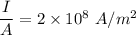
We need to find the resistivity of this wire. We know that,
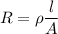
Where
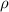 is the resistivity of wire
is the resistivity of wire
Also,
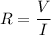
So,
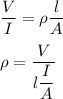
Put all the values,
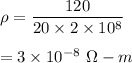
So, the resistivity of this wire is equal to
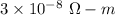 .
.