Answer: The parent isotope is undergoing alpha decay.
Step-by-step explanation:
A nuclear reaction is defined as the reaction in which the changes in the nucleus of an atom take place and usually form a different element. An unstable nucleus undergoes various decay processes to attain stability.
Alpha decay is a type of decay process that happens when a heavy nucleus decays into a light nucleus with the release of an alpha particle. This alpha particle carries a charge of +2 units and has a mass of 4 units. It is also known as the helium nucleus. The general equation for this decay process is:
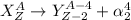
It is given that the daughter isotope formed has atomic number 2 less than the parent isotope. Thus, it is undergoing alpha decay.