Considering the definition of an equation and the way to solve it, the integer is 5.
An equation is the equality existing between two algebraic expressions connected through the equals sign in which one or more unknown values, called unknowns, appear in addition to certain known data.
The members of an equation are each of the expressions that appear on both sides of the equal sign while the terms of an equation are the addends that form the members of an equation.
The solution of a equation means determining the value that satisfies it. In this way, by changing the unknown to the solution, the equality must be true.To solve an equation, keep in mind:
- When a value that is adding, when passing to the other member of the equation, it will subtract.
- If a value you are subtracting goes to the other side of the equation by adding.
- When a value you are dividing goes to another side of the equation, it will multiply whatever is on the other side.
- If a value is multiplying it passes to the other side of the equation, it will pass by dividing everything on the other side.
In this case, twice the square of an integer is five less than eleven times the integer.
Let's call the variable "integer" x.
Knowing that:
- "Twice the square of x = five less than eleven times x"
- The square of x is x².
- "Twice" means to multiply by 2.
- "Eleven times" is multiplication by 11
- "Five less than eleven times x" indicates that you should subtract 5 from 11x.
the equation is:
2x²= 11x -5
Solving:
2x² - 11x + 5 = 0
Being this a quadratic function of the form ax² + by +c, then it can be solved by:
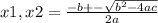
In this case, being a=2, b=-11 and c=5, the equation is solved by:
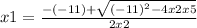
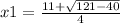
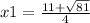
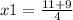
x1=20÷4
x1=5
and
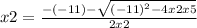
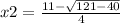

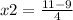
x2=2÷4
x2= 1/2
x is an integer and 1/2 is not an integer, but 5 is. Therefore the integer is 5.