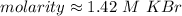Answer:

Step-by-step explanation:
Molarity is a measure of concentration in moles per liter.
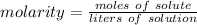
1. Find Formula for Compound
We have the compound potassium bromide. Potassium (K) has an oxidation state of +1 and bromine (Br) has -1. They bond in a 1:1 ratio, so the formula is KBr.
2. Convert Grams to Moles
We are given the amount of solute in grams, but we need moles. To convert, we use the molar mass. These values are found on the Periodic Table. They are the same as the atomic masses, but the units are grams per moles (g/mol) instead of atomic mass units (amu).
Look up the individual element's molar mass.
- Potassium: 39.098 g/mol
- Bromine: 79.90 g/mol
The formula of KBr contains no subscripts, so we can add the molar masses.
- KBr: 39.098+ 79.90 =118.99 g/mol
Use the molar mass as a ratio.
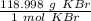
We want to convert 25.3 grams, so we multiply by that value.
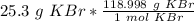
Flip the ratio so the units of grams of KBr cancel.
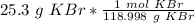
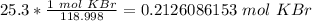
3. Convert Milliliters to Liters
Molarity uses liters, so we must convert the 150 milliliters. 1 liter contains 1000 milliliters.
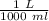
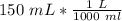
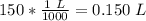
4. Calculate Molarity
Now we have the moles of solute and liters of solution, so we can find molarity.
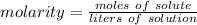
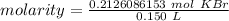
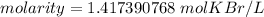
The original measurements had 3 significant figures, so our answer must have the same. For the number we found, that is the hundredth place. The 7 in the thousandth place tells us to round the 1 to a 2.
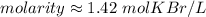
1 mole per liter is equal to 1 Molar (M), so we must convert the units.