Answer: The balanced equation for the complete oxidation reaction that occurs when methane (CH4) burns in air is
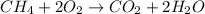 .
.
Step-by-step explanation:
When a substance tends to gain oxygen atom in a chemical reaction and loses hydrogen atom then it is called oxidation reaction.
For example, chemical equation for oxidation of methane is as follows.
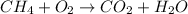
Number of atoms present on reactant side are as follows.
Number of atoms present on product side are as follows.
To balance this equation, multiply
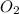 by 2 on reactant side. Also, multiply
by 2 on reactant side. Also, multiply
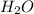 by 2 on product side. Hence, the equation can be rewritten as follows.
by 2 on product side. Hence, the equation can be rewritten as follows.
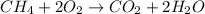
Now, the number of atoms present on reactant side are as follows.
Number of atoms present on product side are as follows.
Since, the atoms present on both reactant and product side are equal. Therefore, this equation is now balanced.
Thus, we can conclude that balanced equation for the complete oxidation reaction that occurs when methane (CH4) burns in air is
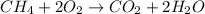 .
.