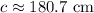The length of other leg is :
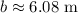
The length of hypotenuse of right triangle is :
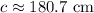
To solve both problems, we can use the Pythagorean theorem, which states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (c) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides (a and b):
![\[ c^2 = a^2 + b^2 \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/x08o5bqdjdbmrqhh1uwemj1cj90ns3rfhs.png)
For problem #1:
Given the hypotenuse c = 8 m and one leg a = 5.2 m, we can find the length of the other leg b using the rearranged Pythagorean theorem:
![\[ b = √(c^2 - a^2) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/l0ue4k4ftqzv268j20biriadt24pelqsln.png)
We will calculate this to find the length of the other leg, rounding to the nearest hundredth.
For problem #2:
Given the two legs a = 136 cm and b = 119 cm, we can find the hypotenuse c using the Pythagorean theorem:
![\[ c = √(a^2 + b^2) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/vke989w3qr8ov5xdtown0a8zazwceolhqo.png)
We will calculate this to find the length of the hypotenuse, rounding to the nearest tenth.
Let's do these calculations.
For problem #1, the length of the other leg of the right triangle is 6.08 m when rounded to the nearest hundredth.
For problem #2, the length of the hypotenuse of the right triangle is 180.7 cm when rounded to the nearest tenth. Here are the step-by-step calculations for each:
**Problem #1**:
1. Use the Pythagorean theorem:
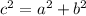
2. Rearrange to solve for the missing leg:
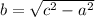
3. Substitute the known values:
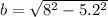
4. Calculate and round to the nearest hundredth:
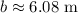
Problem #2:
1. Use the Pythagorean theorem:
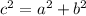
2. Substitute the known values:
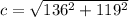
3. Calculate and round to the nearest tenth: