Answer:

Step-by-step explanation:
In a neutralization reaction, an acid and base react to form salt and water. The hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH-) combine to form water, while the other spectator ions bond to make salt.
For this reaction, the acid is HCl (hydrochloric acid) and NaOH (sodium hydroxide).
The H (from HCl) and OH (from NaOH) combine to make water (HOH or H₂O). The other ions, Cl and Na combine to form NaCl or sodium chloride. Let's write the neutralization reaction.
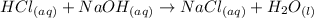
Now let's perform the calculation. We should use the titration equation or:
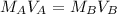
where M is the molarity of the acid or base and V is the volume.
We know there are 25 milliliters of 1 molar HCl (acid) and an unknown volume of 2 molar NaOH (base).
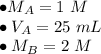
Substitute the known values into the formula.
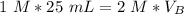
Since we are solving for the volume of the base, we must isolate the variabel. it is being multiplied by 2 M and the inverse of multiplication is division. Divide both sides by 2 M.
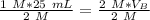
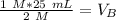
The units of M cancel.
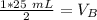
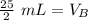
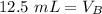
12.5 milliliters of 2 M sodium hydroxide are required to neutralize 25 mL of 1 M hydrochloric acid.