Answer:
C. 7370 joules.
Step-by-step explanation:
There is a mistake in the statement. Correct form is described below:
Using the above data table and graph, calculate the total energy in Joules required to raise the temperature of 15 grams of ice at -5.00 °C to water at 35 °C.
The total energy needed to raise the temperature is the combination of latent and sensible heats, all measured in joules, and represented by the following model:
![Q = m\cdot [c_(i) \cdot (T_(2)-T_(1))+L_(f) + c_(w)\cdot (T_(3)-T_(2))]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/high-school/bbntribd5p9f2olnfpqlwtzhyzxhxbkywu.png) (1)
(1)
Where:
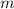 - Mass of the sample, in grams.
- Mass of the sample, in grams.
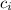 - Specific heat of ice, in joules per gram-degree Celsius.
- Specific heat of ice, in joules per gram-degree Celsius.
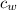 - Specific heat of water, in joules per gram-degree Celsius.
- Specific heat of water, in joules per gram-degree Celsius.
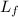 - Latent heat of fusion, in joules per gram.
- Latent heat of fusion, in joules per gram.
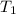 - Initial temperature of the sample, in degrees Celsius.
- Initial temperature of the sample, in degrees Celsius.
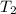 - Melting point of water, in degrees Celsius.
- Melting point of water, in degrees Celsius.
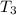 - Final temperature of water, in degrees Celsius.
- Final temperature of water, in degrees Celsius.
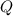 - Total energy, in joules.
- Total energy, in joules.
If we know that
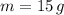 ,
,
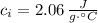 ,
,
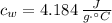 ,
,
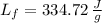 ,
,
 ,
,
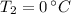 and
and
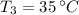 , then the final energy to raise the temperature of the sample is:
, then the final energy to raise the temperature of the sample is:
![Q = (15\,g)\cdot \left[\left(2.06\,(J)/(g\cdot ^(\circ)C) \right)\cdot (5\,^(\circ)C)+ 334.72\,(J)/(g) + \left(4.184\,(J)/(g\cdot ^(\circ)C)\right)\cdot (35\,^(\circ)C) \right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/high-school/aadrg58w9i0ujl7tiwmg5g6o0dhjovabd5.png)
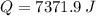
Hence, the correct answer is C.