Answer:
1. This reaction is (A) Exothermic .
2. When the temperature is decreased the equilibrium constant, K: (A) Increases
3.When the temperature is decreased the equilibrium concentration of Co2: (A) Increases
Step-by-step explanation:
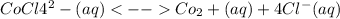
1. The pink color predominates at low temperatures, indicating that the commodity is preferred.
This is a reaction that is exothermic.
2. As the decrease in the temperature , the equilibrium constant , K ;
equilibrium constant =
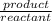 =
=
![([CO^2^+][Cl^-^4])/(CoCl^2^-_4)](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/6pjf1fccx68fz85tlikub1803pv7mjvsvs.png)
As the temperature drops, the concentration of
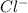 and
and
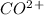 rises, and K rises as well , thus it increases .
rises, and K rises as well , thus it increases .
3. The equilibrium concentration of
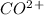 decreases as the temperature decreases:
decreases as the temperature decreases:
When the temperature is lowered, the equilibrium shifts to the right , that is it increases.