Answer:
a) the reflective surface has twice the energy transfer
b) A = 1.3 10²⁷ km²
c) the energy emitted by the sun is distributed in a sphere that depends on the square of the distance, and the gravitational force depends on the square of the distance
Step-by-step explanation:
a) The pressure exerted on the candle is related to the variation of the momentum
P =
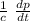
in a case of absorption (inelastic shock) all the energy is absorbed therefore the pressure is
P = \frac{1}{c} \ \frac{dp}{dt}
in the case of reflection (elastic shock) an energy is absorbed by absorbing the light and then by action and reaction the same energy is absorbed in the reflected light
P = 2 \frac{1}{c} \ \frac{dp}{dt}
In conclusion, the reflective surface has twice the energy transfer.
b) pressure is defined with force per unit area
P = F / A
F = P A
this force must be greater than the gravitational force of attraction of the sun
Fg = G m Ms / r²
let's look for the case that the two forces are equal
F = Fg
P A_sail = G m Ms = r²
suppose a fully reflective sail
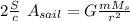
The pointing vector is the power delivered per unit area
S = I = P / A
where A is the area of the sphere where the is distributed by the sun
A = 4π r²
we substitute
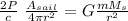
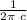 A_{sail} = G m M_s
A_{sail} = G m M_s
A = G m M_s 2π c
let's calculate
A = 6.67 10⁻¹¹ 10000 2 10³⁰ 2π 3 10⁸
A = 1,257 10³³ m²
let's reduce to km²
A = 1.3 10³³ m² (1km / 10³ m) ²
A = 1.3 10²⁷ km²
c) The size of the candle is independent of the distance to the sun because the energy emitted by the sun is distributed in a sphere that depends on the square of the distance, and the gravitational force depends on the square of the distance, therefore the two dependencies are canceled.