Answer: The equilibrium partial pressure of
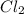 is 0.964 atm.
is 0.964 atm.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
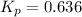
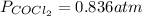
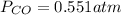
The given reaction equation is as follows.
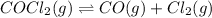
Formula used to calculate the partial pressure of
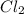 is as follows.
is as follows.
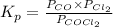
Substitute the values into above formula as follows.
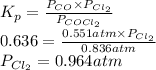
Thus, we can conclude that the equilibrium partial pressure of
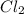 is 0.964 atm.
is 0.964 atm.