Answer:
The thermal energy gained by the water during the entire process is 90,372 J
Step-by-step explanation:
Given;
mass of the ice cube, m = 30 g
latent heat of fusion of ice, L = 334 J/g
specific heat capacity of water, C = 4.184 J/g⁰C
latent heat of vaporization of water, h = 2260 J/g
The thermal energy gained by the water during the entire process is calculated as;
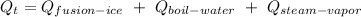
The heat of fusion of the ice at 0⁰C is calculated as;
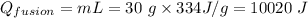
The heat of capacity of the water from 0⁰C to 100 ⁰C
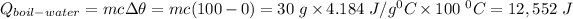
The heat of vaporization of the steam at 100⁰C is calculated as;
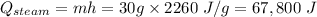
The thermal energy gained by the water during the entire procees;
Qt = 10,020 J + 12,552 J + 67,800 J
= 90,372 J
Therefore, the thermal energy gained by the water during the entire process is 90,372 J