Answer:
The heat at constant pressure is -3,275.7413 kJ
Step-by-step explanation:
The combustion equation is 2C₆H₆ (l) + 15O₂ (g) → 12CO₂ (g) + 6H₂O (l)
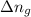 = (12 - 15)/2 = -3/2
= (12 - 15)/2 = -3/2
We have;
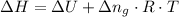
Where R and T are constant, and ΔU is given we can write the relationship as follows;
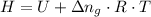
Where;
H = The heat at constant pressure
U = The heat at constant volume = -3,272 kJ
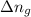 = The change in the number of gas molecules per mole
= The change in the number of gas molecules per mole
R = The universal gas constant = 8.314 J/(mol·K)
T = The temperature = 300 K
Therefore, we get;
H = -3,272 kJ + (-3/2) mol ×8.314 J/(mol·K) ×300 K) × 1 kJ/(1000 J) = -3,275.7413 kJ
The heat at constant pressure, H = -3,275.7413 kJ.