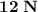Answer:
The magnitude of the electrostatic force on
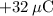 is:
is:
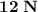
Step-by-step explanation:
Consider
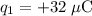 is at position
is at position
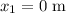
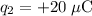 is at position
is at position
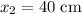
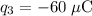 is at position
is at position
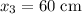
The sum of all horizontal forces on
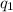 is given as
is given as
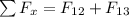
where
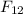 is the force exerted by
is the force exerted by
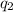
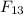 is the force exerted by
is the force exerted by
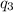
The force on
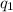 exerted by
exerted by
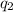 is repulsive, so the direction of the force
is repulsive, so the direction of the force
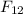 is to the left (negative direction). Thus
is to the left (negative direction). Thus
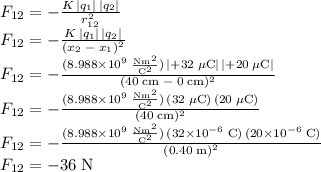
The force on
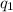 exerted by
exerted by
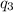 is attractive, so the direction of the force
is attractive, so the direction of the force
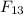 is to the right (positive direction). Thus
is to the right (positive direction). Thus
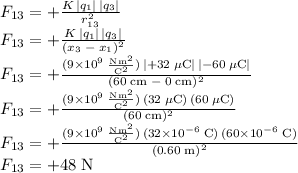
Therefore

the electrostatic force on
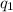 is to the right and has a magnitude of
is to the right and has a magnitude of