Answer:
x = - 2, x = 1
Explanation:
Given
f(x) =
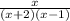
The denominator cannot be zero as this would make f(x) undefined.
Equating the denominator to zero and solving for x gives the values that x cannot be and if the numerator is non zero for these values then they are vertical asymptotes.
(x + 2)(x - 1) = 0
x + 2 = 0 ⇒ x = - 2
x - 1 = 0 ⇒ x = 1
Vertical asymptotes occur at x = - 2 and x = 1