Answer:
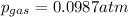
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello there!
In this case, according to this problem about partial pressures, we first use the Dalton's law in order to realize how the vapor pressure of water and the partial pressure of the gas contribute to the total pressure:
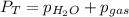
Thus, since the vapor pressure of water at 25 °C is 0.0313 atm, the partial pressure of the gas turns out to be:
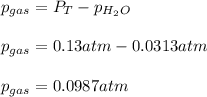
Regards!