Answer:
A. Q = 2.74 x 10⁷ J = 27.4 MJ
B. E = 3.91 x 10⁸ J = 391 MJ
Step-by-step explanation:
A.
Heat rejected can be found as follows:
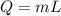
where,
Q = Heat rejected = ?
m = mass = 82.1 kg
L = Latent Heat of fusion = 334000 J/kg
Therefore,
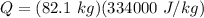
Q = 2.74 x 10⁷ J = 27.4 MJ
B.
First, we will calculate the efficiency of the Carnot Cycle as follows:
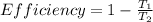
where,
T₁ = Heat intake temperature = 0°C + 273 = 273 k
T₂ = Heat rejection temperature = 20.6°C + 273 = 293.6 k
Therefore,
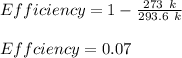
Therefore, the energy input required is:
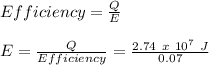
E = 3.91 x 10⁸ J = 391 MJ