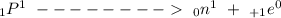Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
(a) Electron Emission (Beta- decay):
When an unstable nucleus decays by the emission of Beta- particle, its charge number ‘Z’ increases by 1 but, its mass number ‘A’ remains unchanged. The transformation is represented by the equation:

It is called ‘Negative Beta Decay’. It is more common than alpha decay.
Example:
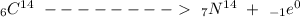
Note:
There are no electrons in a nucleus so, with the emission of a particle, one of the neutrons is converted to a proton and an electron.

(b) Positron Emission (Beta+ decay):
When an unstable nucleus decays by the emission of the positron, its charge number ‘Z’ decreases by 1 but, its mass number ‘A’ remains unchanged. The transformation is represented by the equation:

Examples:

Note:
Inside the nucleus, only a proton can be transformed into a neutron with the emission of a positron (anti-particle of electron)