Answer:
0.078
Step-by-step explanation:
The equation is :
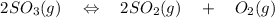
Initial 0.948 ----- ----
Change -2x +2x +x
Final 0.369 2x x
So the total pressure must reman same = 0.948
And the total pressure = partial pressure of all gases
0.948 = ( 0.369 + 2x + x )
0.948 = 0.369 + 3x
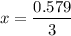
= 0.193 atm
So the partial pressure of
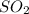 = 0.193 x 2
= 0.193 x 2
= 0.386 atm
Partial pressure of
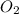 = 0.193 atm
= 0.193 atm
Therefore,
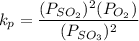
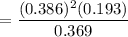
= 0.078