Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
The reaction is given as:
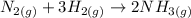
The reaction quotient is:
![Q_C = ([NH_3]^2)/([N_2][H_2]^3)](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/1a745h9ii449yugm4sx62esjmxtabhrnse.png)
From the given information:
TO find each entity in the reaction quotient, we have:
![[NH_3] = (6.42 * 10^(-4))/(3.5)\\ \\ NH_3 = 1.834 * 10^(-4)](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/g52vb69572ucgpxayu506y9qi6639pkxjh.png)
![[N_2] = (0.024 )/(3.5)](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/rdc5hsxgi1zjie49ftl6bfbldapooi9wx2.png)
![[N_2] = 0.006857](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/6hw80qt3gyn19nxpx9p5zawpb8xs1rbp6v.png)
![[H_2] =(3.21 * 10^(-2))/(3.5)](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/zxbi0xayk229pdjv6ajac303gd8gut6h8y.png)
![[H_2] = 9.17 * 10^(-3)](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/hr17xkt8wy2xac0ya1vcp5qsu3lmi6vsgr.png)
∴
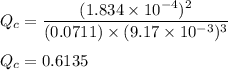
However; given that:
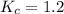
By relating
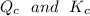 , we will realize that
, we will realize that
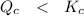
The reaction is said that it is not at equilibrium and for it to be at equilibrium, then the reaction needs to proceed in the forward direction.