Answer:
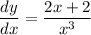
Explanation:
we would like to figure out the derivative of the following:
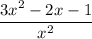
to do so, let,
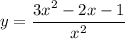
By simplifying we acquire:
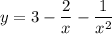
use law of exponent which yields:
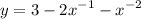
take derivative in both sides:
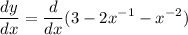
use sum derivation rule which yields:
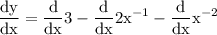
By constant derivation we acquire:
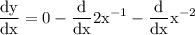
use exponent rule of derivation which yields:
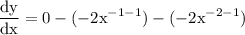
simplify exponent:
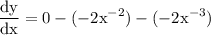
two negatives make positive so,
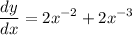
further simplification if needed:
by law of exponent we acquire:
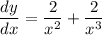
simplify addition:
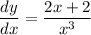
and we are done!